Digital transformation has become one of those buzzwords, but what does it actually mean? Generally speaking, it refers to digitizing business processes to more efficiently solve business problems and more effectively serve customers through online channels. Moving to the cloud is typically a key component of this transformation.
By 2024, more than 45% of IT spending on system infrastructure, infrastructure software, application software and business process outsourcing will shift from traditional solutions to cloud.
— “Cloud Shift Impacts All IT Markets,” Gartner, Oct 26, 2020
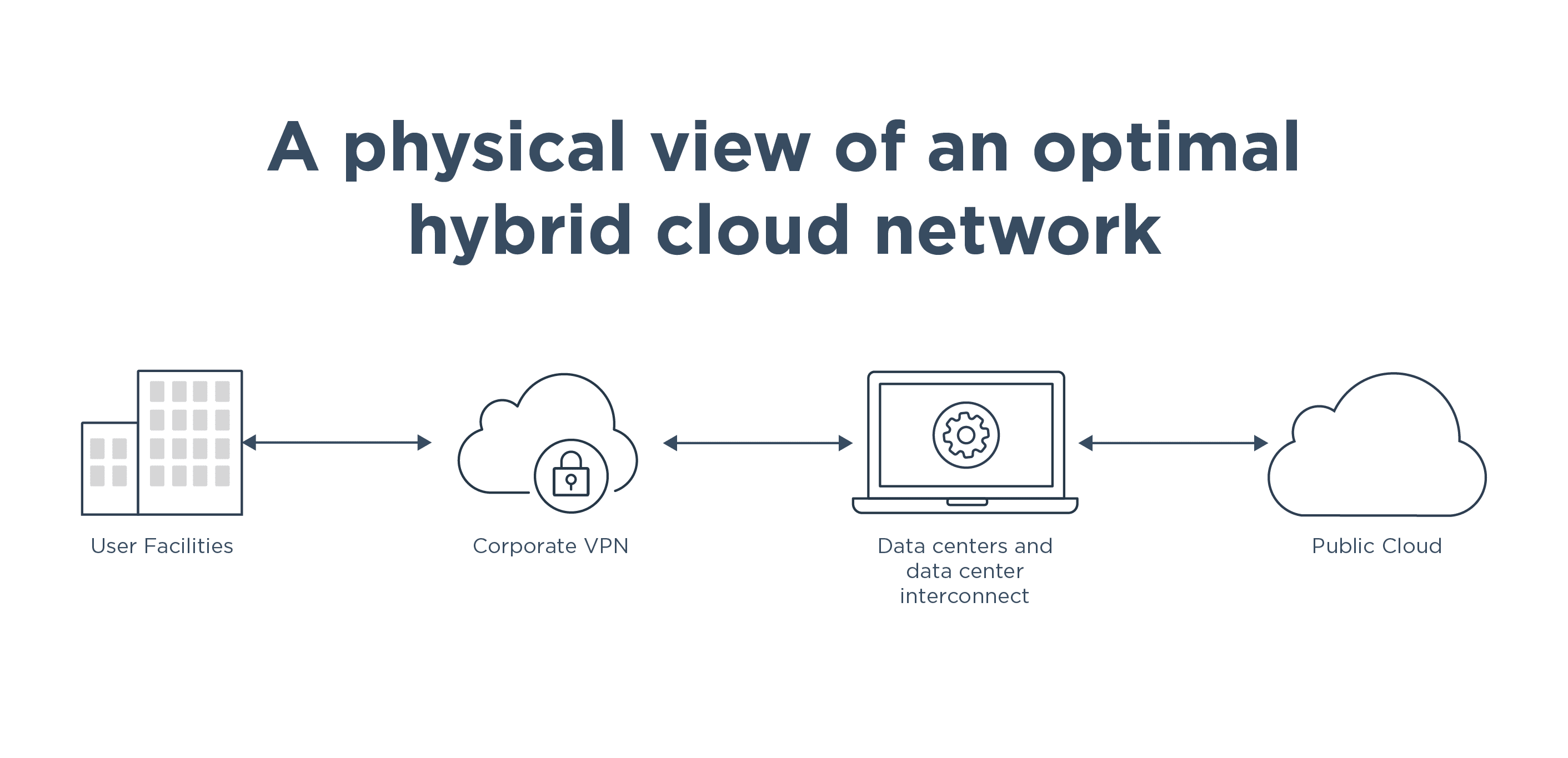
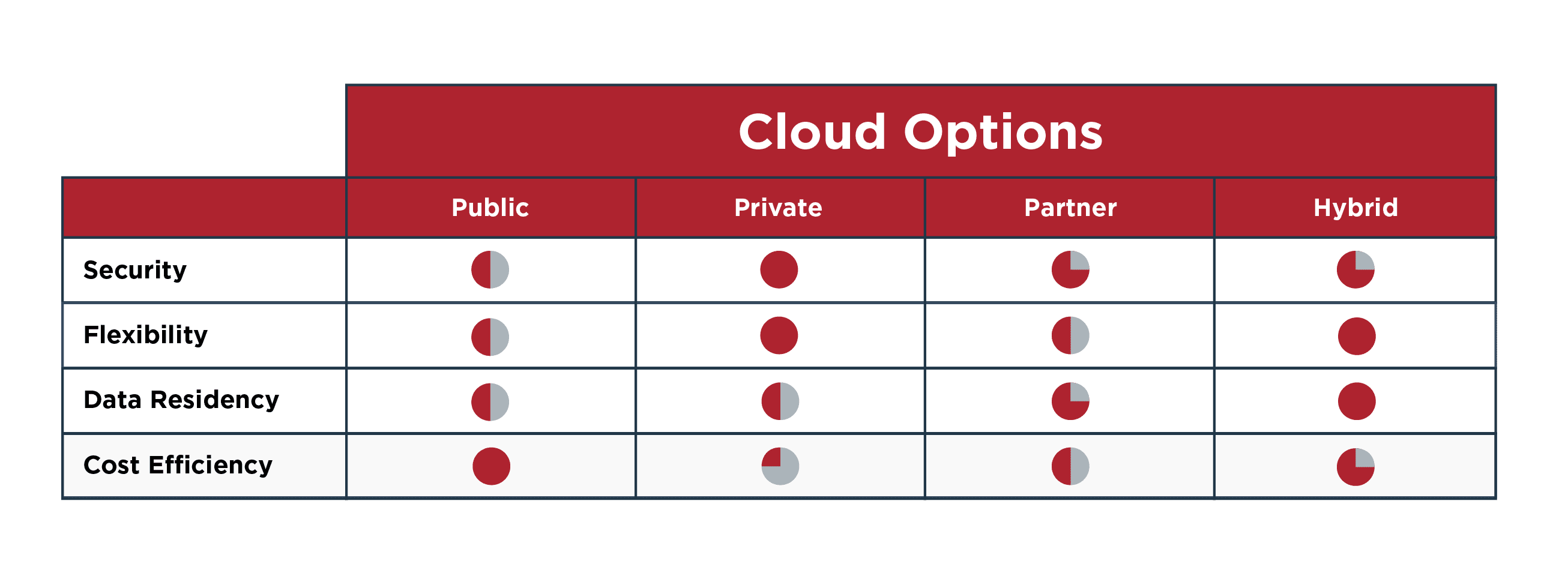
For many enterprises, moving to the cloud actually means moving to multiple clouds. A hybrid cloud infrastructure is often chosen because it provides organizations with the ultimate in flexibility, cost efficiency and agility. But a hybrid cloud approach can also create security vulnerabilities if it’s not carefully architected.
According to the 2020 Verizon Data Breach Incident Report, misconfiguration of cloud services is the second largest cause of breaches, eclipsed only by hacking. For example, MGM Resorts’ breach in 2020 was the result of unauthorized access to a cloud server and resulted in leaked account information for upwards of 10 million users.
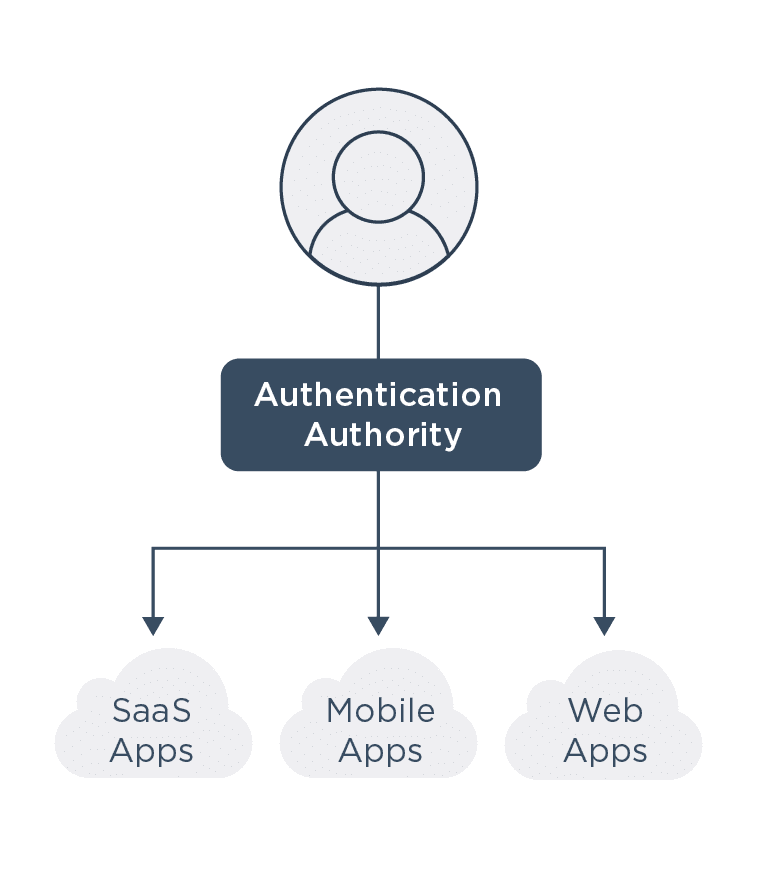
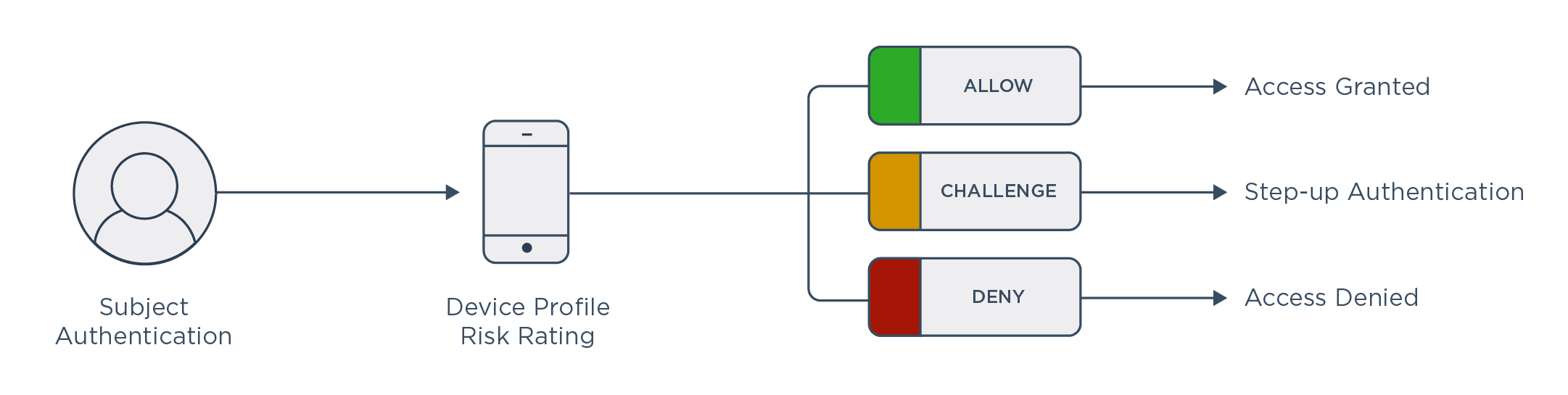
While cloud migration does alter the threat landscape, security vulnerabilities aren’t a foregone conclusion. With more entry points available to users and bad actors, organizations are finding better identity and authentication approaches to enhance security. This is where identity and access management (IAM) steps in to protect access to resources hosted and managed across hybrid cloud environments.