In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven business landscape, maintaining robust security and compliance protocols is paramount. One critical concept that organizations adopt to safeguard their operations is Segregation of Duties (SoD). Read on to understand what Segregation of Duties is, why Segregation of Duties is an important policy in today’s world, and how modern tools and technologies can facilitate its effective implementation.
What is Segregation of Duties?
Definition of Segregation of Duties (SoD)
Segregation of Duties, sometimes called Separation of Duties, is a fundamental internal control principle that involves dividing tasks and responsibilities among different individuals to reduce the risk of errors, fraud, and unauthorized actions. By ensuring that no single person has control over all aspects of any critical business process, organizations can enhance their security and compliance posture.
Segregation of Duties is a broader practice that has evolved over time, becoming an industry standard in the world of identity, specifically as it relates to compliance efforts in minimizing toxic access. It is recognized and mandated by various regulatory bodies to ensure that organizations uphold the highest levels of operational integrity.
The Importance of Segregation of Duties
Risk Mitigation
At its core, segregation of duties is about risk mitigation. By distributing responsibilities, organizations can prevent any one individual from having unchecked power over crucial processes, thus minimizing toxic access combinations. This distribution minimizes the potential for and operational errors, thereby safeguarding an organization’s assets and reputation.
Preventing Fraud and Errors
When responsibilities are shared, the likelihood of intentional fraud or inadvertent errors decreases significantly. For example, in financial operations, separating the duties of authorizing transactions, recording transactions, and maintaining custody of assets ensures that no single employee can manipulate the process for personal gain without being detected.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries are subject to stringent regulatory requirements that mandate the implementation of SoD controls. Regulations such as Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) in the United States require organizations to establish and maintain an adequate internal control structure. SoD plays a crucial role in meeting these compliance standards, thereby avoiding legal penalties and maintaining stakeholder trust.
Enhancing Security
A robust SoD framework strengthens an organization’s security posture. By clearly defining and enforcing roles and responsibilities, it minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and activities. This principle aligns with the broader security strategy of enforcing the principle of least privilege, ensuring that individuals have access only to the information and systems necessary for their roles.
Benefits of Implementing Segregation of Duties
Reduced Risk of Fraud
Implementing SoD reduces the risk of fraud by ensuring that critical tasks are not concentrated in the hands of a single individual. This distribution makes it challenging for anyone to engage in fraudulent activities without detection, as the system inherently provides checks and balances.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Contrary to the perception that SoD might slow down processes, it can actually enhance operational efficiency. Automated systems and workflows can streamline the enforcement of SoD policies, reducing the need for manual interventions and the risk of human error.
Maintained Compliance
By implementing SoD, organizations can simplify the process of meeting regulatory requirements. Creation of policy around segregation of duties allows for automated enforcement and detailed audit trails to ensure that compliance is maintained consistently and transparently, facilitating smoother audits and inspections.
Core Components of Segregation of Duties
LCM as a Starting Component
Lifecycle Management (LCM) serves as a critical starting point for implementing segregation of duties within an organization and for a broader identity governance platform. It involves defining and managing user identities, roles, organizations, and access permissions throughout their lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding for employees, business partners, and contractors.
Preventative Controls in Access Request
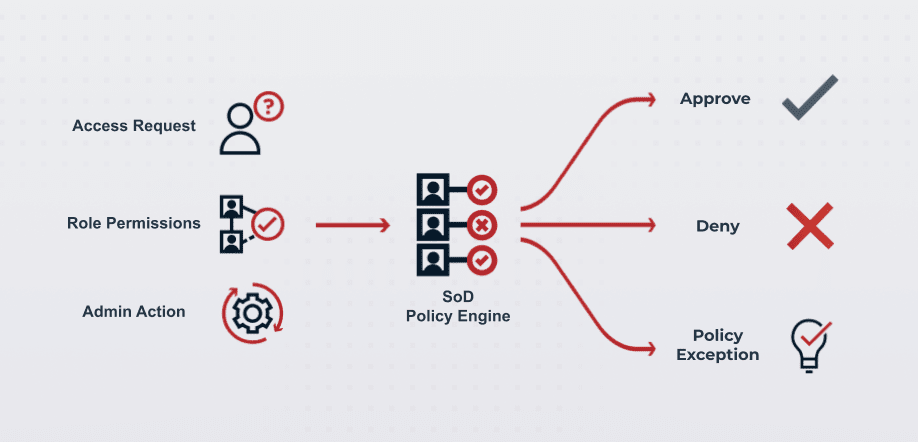
Defining clear policies is essential for preventing toxic access combinations across the organization. Policies should outline the roles and responsibilities, access controls, and segregation rules to prevent conflicts of interest and ensure compliance. Specifically, an SoD policy engine should be able to:
Automatically deny access requests for toxic access combinations in line with policy
Verify role permissions at time of access request for more context on the request to dynamically route approvals appropriately
Give admins the tools to manage exceptions where they might need to exist
Policy Centralization for Detective Controls
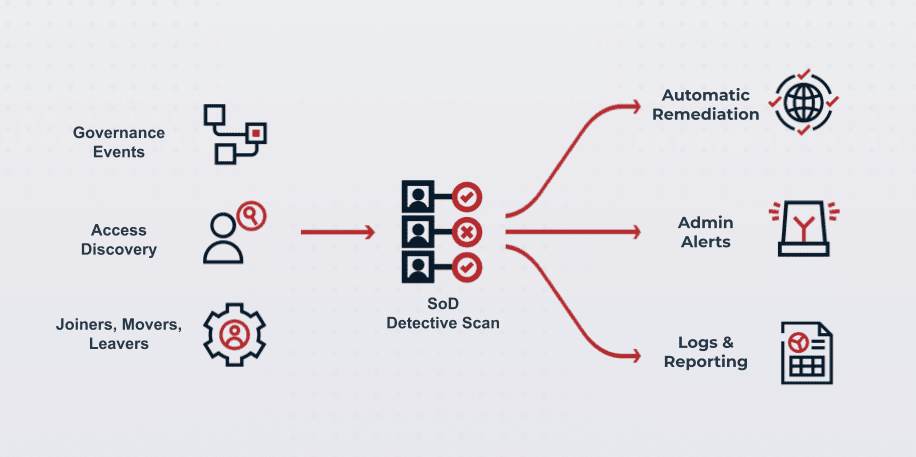
Regular scanning of the organizational environment is necessary to identify existing toxic access combinations or access that requires review. Detective controls can continuously monitor user activities, generating alerts for suspicious actions and enabling timely intervention. Detective controls within Segregation of Duties often take the form of:
Orchestration workflows and governance events to route access requests appropriately when non-appropriate access is requests
Access discovery for admins, allowing for the comprehensive scan over your IGA estate for where access is in need of review or toxic access may exist today
JML processes, flagging for admins where toxic access may be a concern for the organization, especially as employees move between roles
Technologies and Tools for Effective Segregation of Duties
AI and Machine Learning
Leveraging AI and machine learning can enhance the effectiveness of SoD by automating access reviews and approvals. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, ensuring that access controls are both efficient and effective.
Identity Workflows
Governance events can trigger identity workflows to automate the enforcement of SoD policies. These workflows streamline approval processes, ensure compliance with policies, and reduce the administrative burden on IT and security teams.
Self-Service and Automation
Empowering users with self-service access requests and automated workflows simplifies the management of SoD. Users can request access as needed, while automated systems ensure that these requests are reviewed and approved according to SoD policies.
Future Trends in Segregation of Duties
Integration with Zero Trust Models
As organizations adopt Zero Trust security models, SoD will play an integral role. Attributes can serve as triggers for governance events, ensuring that access controls are enforced dynamically and in real-time.
Enforcing Zero Standing Privilege
Zero Standing Privilege is a principle that aligns with SoD by granting permissions on a just-in-time and just-as-needed basis. This approach ensures that users have only the access they need, when they need it, and for the duration required, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Advancements in AI and Automation
The future of SoD will see increased reliance on AI and automation. These technologies will enable more sophisticated and efficient enforcement of SoD policies, reducing the risk of human error and improving overall security.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
As regulatory requirements continue to evolve, SoD will remain a critical component of compliance strategies. Organizations must stay abreast of changes in regulations and adjust their SoD policies and practices accordingly.
Conclusion
In summary, Segregation of Duties is a vital concept for organizations aiming to enhance their security, compliance, and operational efficiency. By distributing responsibilities, defining clear policies, and leveraging modern technologies, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and uphold the highest standards of integrity.
For more detailed information on Segregation of Duties and how Ping Identity Governance can help your organization implement these controls, please refer to our comprehensive Segregation of Duties Datasheet.