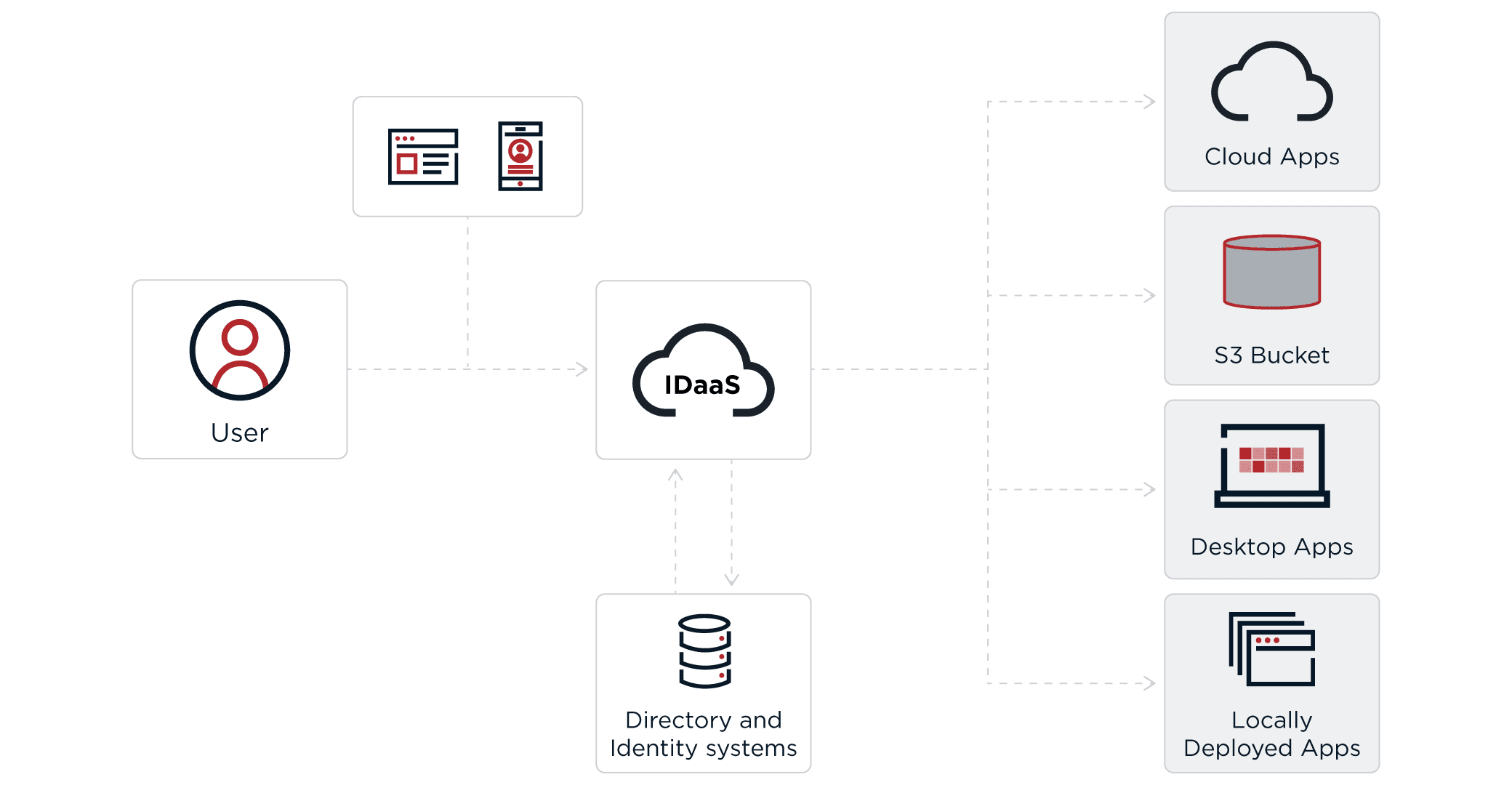
IDaaS platforms offer various capabilities to secure and manage user identities across cloud and on-premise applications. Below are the key types of IDaaS solutions:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA IDaaS solutions are designed to secure user logins by requiring more than just a username and password. These platforms offer adaptive MFA that evaluates the risk of each login attempt and triggers additional authentication steps such as biometrics, one-time passcodes, or push notifications. MFA IDaaS ensures that even if a password is compromised, unauthorized access is still prevented, significantly reducing the risk of identity theft and breaches.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
SSO IDaaS solutions simplify the user authentication process by allowing users to log in once and gain access to multiple applications and systems without needing to re-enter credentials. This centralized authentication service not only improves user experience but also helps IT departments by streamlining access management and reducing the overhead of password resets. SSO enhances both security and productivity by ensuring consistent and secure access to cloud and on-premises resources.
Directory Services
Directory services in an IDaaS context provide cloud-based directory management for storing and organizing user identities and resources. These platforms act as the central hub for managing user profiles, roles, permissions, and access to various applications. Cloud directories integrate seamlessly with other identity management solutions and support scalability, enabling organizations to efficiently handle identity management across distributed environments while maintaining security and compliance standards.
Overview of IDaaS Capabilities and Configurations
From a user's point of view, IDaaS provides similar capabilities to an on-premises deployment of identity and access management, assuming the user has access to the IDaaS cloud solution. The biggest difference is that IDaaS is hosted in the cloud by a third-party provider, which allows users to securely access their account from anywhere via different devices. This is done through a combination of single sign-on, multi-factor authentication and directory solutions.
There are many different types of IDaaS solutions. Some IDaaS providers support only one piece of the puzzle (e.g., providing only a directory) while other IDaaS providers deliver a more comprehensive suite of functionality encompassing multiple pieces of the puzzle (e.g., combined SSO, MFA and directory).
In addition to these different configurations of IDaaS solutions, different categories of IDaaS cater to different end users. Classes of end users include customers, employees and business partners.
Basic IDaaS
Basic IDaaS solutions are well-suited for small businesses or organizations that primarily use cloud-based applications and have minimal on-premises infrastructure. These solutions are lightweight, easy to implement, and cost-effective, offering essential identity management features that are ideal for companies with straightforward IT needs.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Cloud-Focused: Primarily designed for cloud applications, making integration with SaaS platforms (e.g., Office 365, Salesforce) seamless and straightforward.
- Simplified User Management: Provides intuitive, user-friendly interfaces and setup wizards, enabling fast onboarding and minimal administrative overhead.
- Basic Security: Includes simple multi-factor authentication (MFA) options like SMS, email, or mobile app-based tokens for securing user access to cloud apps.
- Scalability: Suitable for SMBs, providing flexibility to scale as the organization grows without complex infrastructure requirements.
- Minimal Customization: Out-of-the-box configurations and standard policies are typically enough for small businesses, with fewer customization options.
Enterprise IDaaS
Enterprise IDaaS is tailored for large organizations with complex, hybrid IT environments, where integrating on-premises systems, cloud platforms, and third-party services is crucial. These solutions offer a wide range of advanced features to support intricate access management, enhanced security, and compliance.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Hybrid Environment Integration: Provides seamless connections between on-premises directories (e.g., Active Directory), SaaS applications, and other enterprise systems, supporting both cloud and legacy infrastructures.
- Advanced Security & Compliance: Includes sophisticated multi-factor authentication (MFA) methods like adaptive authentication and biometric verification, as well as robust encryption and auditing tools to meet compliance requirements.
- Granular Access Control: Offers fine-grained access policies such as role-based (RBAC) and attribute-based (ABAC) access control, ensuring users only have access to the resources they need.
- Customizable Workflows and Policies: Enterprise IDaaS platforms allow organizations to customize authentication flows, user provisioning processes, and access policies, offering more flexibility to meet business-specific needs.
- Scalability and Performance: Designed to support large-scale environments, these solutions can handle millions of users, complex integrations, and global access requirements with high performance.
The connectors, bridges and integrations provided by IDaaS solutions for enterprises allow for a more comprehensive solution. This additional functionality is combined with more fine-grained administrative controls to better customize solutions to an enterprise's specific needs.