Short message service (SMS), also known as text messaging, is something you may use every day with your friends and colleagues. Texts sent to your phone can be forwarded or synced with other devices to make sure you never miss a message. SMS can also be used to authenticate a user's identity. Let's look at how SMS authentication works and whether it is secure.
What is SMS Authentication?
What is SMS Authentication?
What is SMS Authentication?
What is SMS Authentication in Two-factor Authentication (2FA) and Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)?
Presenting users with multiple options to verify their identity helps reduce fraud and defend against bad actors. Passwords are the least secure authentication method and can be guessed, stolen or bought on the dark web, so they need to be reinforced. SMS authentication is not typically used as a primary or sole authentication method, but it's commonly used as the second authentication factor in two-factor authentication (2FA) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Authentication types are broken out into three main categories, with SMS authentication falling under the Possession factor:
Knowledge - Something you know. This includes passwords, a PIN (personal identification number), or answers to security questions.
Possession - Something you have. This includes smartphones, mobile devices, security tokens, key fobs and other devices that can either generate or receive one-time passwords (OTPs) or codes.
Biometric - Something you are. This is a physical trait, like a fingerprint or face, that can be scanned for authentication.
How Does SMS Authentication Work?
A one-time password (OTP) is created using an algorithm and sent via text message to a phone number associated with the user. This automatically generated sequence of characters (letters and/or numbers) is valid for a single login session or transaction.

The user copies the OTP to an authentication window that verifies the code with the authentication server to ensure there is a match. If SMS authentication is the final verification method required, the user can now access their account and associated resources. If a third authentication factor is required for multi-factor authentication (MFA), as may be the case for high-value transactions or logins from suspicious IP addresses, access will only be granted after the third proof of identity is provided.
SMS Authentication Codes - Types of One-time Passwords (OTPs)
There are two main types of one-time passwords (OTPs) used as SMS authentication codes. Both use algorithms to generate a new, random code every time a password is requested. Because users do not create these passwords and reuse them on multiple accounts, compromised OTPs have less value to bad actors than traditional passwords.
Time-based one-time password (TOTP) uses time as a moving factor, with passwords typically expiring within 30-240 seconds. If there is a delay in the user receiving a TOTP, such as a slow connection, the TOTP may expire before it can be used and a new one will need to be requested.
HMAC-based one-time password (HOTP) is an event-based password that uses a counter as the moving factor instead of time. HMAC stands for hash-based message authentication code. HOTPs can stay valid for a longer period of time because they aren't time-based.
Is SMS Authentication Secure?
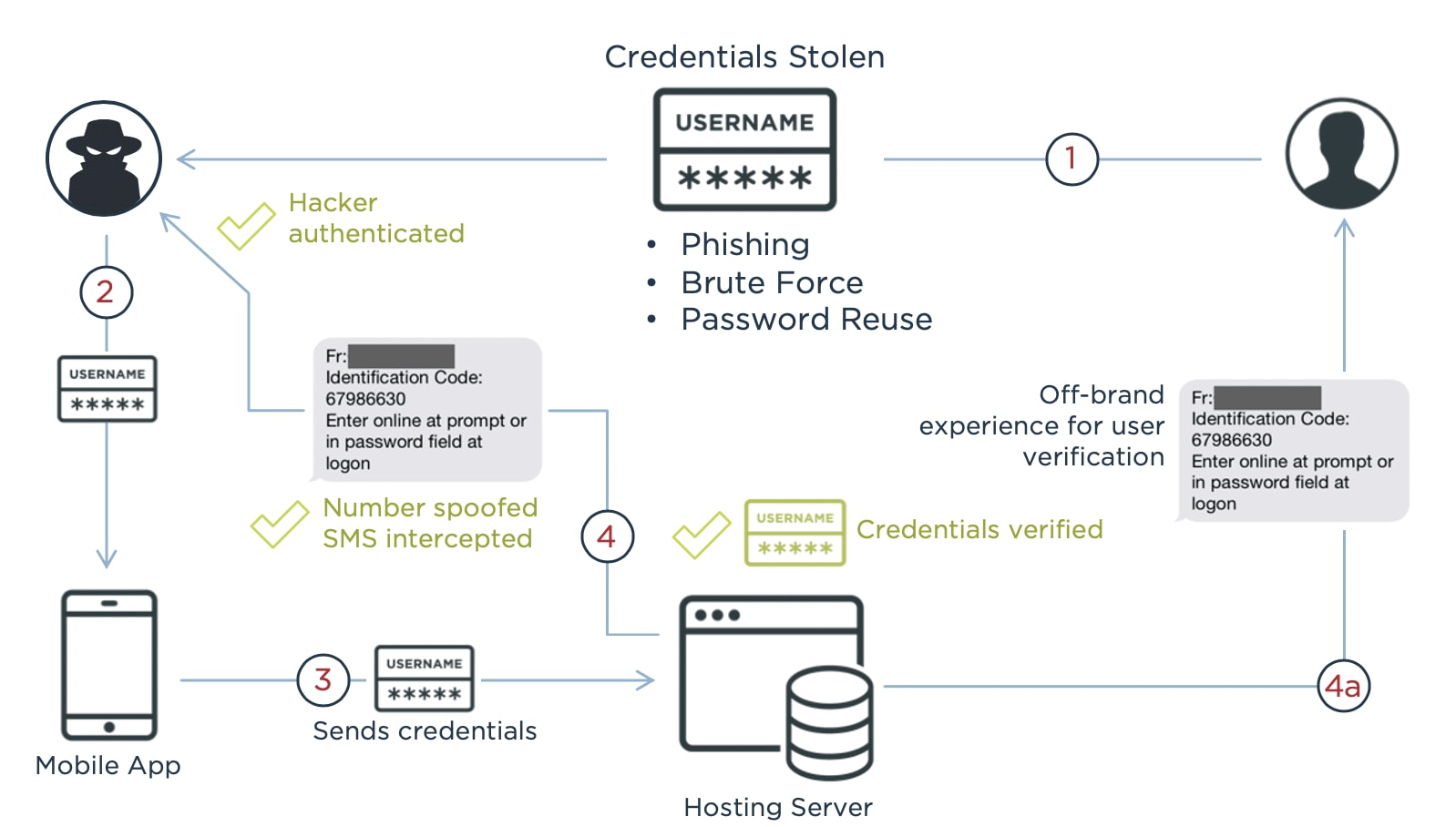
SMS codes can only be used once, making them more secure than passwords. Even so, determined bad actors can still breach a network that uses SMS authentication. For example, hackers used a flaw in Coinbase's account recovery process to get the SMS two-factor authentication token to break into 6,000 customer accounts and transfer funds out of them. They also had access to the email address, password and phone number associated with each account, which may have been stolen through a phishing scheme.
SMS vulnerabilities that can be exploited include:
- SMS messages are sent in clear text and viewable on the user's screen, even a phone's preview screen when the phone is locked.
- SIM swapping is used to fraudulently convince a wireless carrier to assign a phone number to a new SIM card. SIM cards can also be cloned and used in different phones.
- A Signaling System 7 (SS7) attack can be used to intercept text messages.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks can hijack inbound SMS codes or intercept the code being entered on a web page.
- Devices that receive SMS, including phones, tablets and laptops, can be stolen.
For these reasons, SMS authentication is usually combined with other authentication factors to make it more secure.
Is SMS Authentication User-friendly?
Enterprises have to balance convenience and security when deciding which authentication methods to use. This is especially true with customers, who want a seamless and frictionless experience, while also expecting enterprises to keep their accounts and data secure. Frustrated customers can give up and use a competitor after a bad experience.
Since people who have mobile devices are typically familiar with text messages, the learning curve for receiving messages is not as steep as other methods, but users will have to become familiar with the associated authentication windows. There are some additional challenges with SMS authentication, including:
- If it takes too long for the text to arrive, a time-based passcode (TOTP) can expire before use, or users may get frustrated and abandon the experience.
- OTPs can be hard to memorize and are easily mistyped if cut and paste isn't an option.
- A user may have to close a web browser, open an SMS app, copy the OTP, then reopen the web browser, adding too much friction to the process.
There are alternative ways for users to receive OTPs, including mobile-based authenticator apps offered by Ping, Google and Microsoft.
Alternatives to SMS Authentication
While SMS authentication is a huge leap forward from a sole reliance on usernames and passwords, SMS OTPs are not ironclad. Luckily, with constant innovations in the IAM space, there are several good choices for alternate 2FA and MFA approaches.
1. FIDO2
FIDO2 is more than an alternative to SMS authentication. The acronym “FIDO2” refers to new security standards and technologies in the identity industry as developed by the FIDO Alliance. More specifically, the letters stand for “Fast Identity Online” while the number 2 refers to this particular iteration of FIDO alliance standards.
According to their website, “The FIDO Alliance is an open industry association with a focused mission: reduce the world’s reliance on passwords.” As innovations in the identity industry emerge, so do new standards and technologies from the FIDO alliance, such as FIDO2.
FIDO2 Cryptographic Keys: FIDO2 uses “public key cryptography for authentication that is more secure than passwords and SMS OTPs.” These cryptographic keys can be something you possess like a key fob, or authenticated with biometrics like fingerprints on a mobile phone. Regardless of the form that the cryptographic key takes, FIDO2 is predicated on credentials only being stored on a user's device.
2. Mobile Authenticator Apps
On the surface, mobile authenticator apps work in a fashion similar to SMS messaging, but there are some important differences when you look a bit deeper. While both mobile authenticator apps and SMS messaging fall within the “something you have” classification of MFA, SMS has more vulnerabilities.
The most important aspect of mobile authenticator apps is the fact they operate independently of the internet and cellular service. As such, the OTPs generated by authenticator apps are immune from threats like SIM swapping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Authenticator apps are considered extremely secure and are utilized by important organizations like Ping Identity, Microsoft, and Google.
3. Email Authentication
Email authentication is another form of MFA that is used to supplement usernames and passwords. With email authentication, OTPs or magic links are sent directly to a user’s inbox to verify their identity. Email authentication is a popular MFA method that is commonly used to add friction with suspicious activity, like logging in from a new IP address.
Since users must have login credentials to access their email accounts in the first place, email authentication adds an extra layer of security. In turn, email authentication falls in the “something you know” category of MFA. Yet, since email accounts aren’t tied to a specific device like a cryptographic key or authenticator app, they may be compromised by phishing attacks or data breaches.
4. Voice Call Authentication
Voice call authentication is another popular alternative to SMS messaging. With voice call authentication, an OTP is delivered straight to a user’s phone by way of voice messaging. Voice call authentication is another example of a “something you have” MFA method. Whether it be a mobile phone or landline, users prove their identity by having access to the phone number associated with their account.
A major plus for voice call verification is the fact that the OTP is not openly displayed on a screen, so it can’t be compromised by prying eyes. In the event a user misses the original voice call, the OTP will expire and a new one will be generated.
To learn more about different forms of authentication, read our Ultimate Guide to Authentication.
Should You Use SMS Authentication?
Considering the perks and drawbacks of SMS technology begs the question: should you implement SMS authentication in your identity network?
Generally speaking, reinforcing your identity security with MFA practices is always a good idea. However, a key consideration to make is balancing security with convenience during the login process. Too much friction can cause users to abandon your site, while a lack of additional security measures can leave your network vulnerable to attacks.
If your organization is still reliant on traditional login credentials like usernames and passwords, SMS authentication can play a pivotal role in protecting user data. While it might not be the most secure MFA method available, SMS authentication is still extremely effective at stopping fraudulent activity.
For the best possible security posture, it's advisable to include the most secure methods like FIDO2 and mobile authentication apps in your MFA strategy. More often than not, these tools fall within the biometric or possession categories of MFA, while also generating OTPs and/or cryptographic keys that aren’t connected to an outside network.
Frequently Asked Questions
OTP is an acronym that refers to both “one-time passcode” and “one-time password.” OTPs are unique sequences of letters and/or numbers that are generated by algorithms to verify a user’s identity. OTPs can only be used once and generally expire after a certain amount of time - offering unique advantages over traditional credentials like usernames and passwords.
Mobile authenticator apps are considered safer than SMS verification because they operate independently of the internet and cellular service. Because they aren’t reliant upon an outside network to generate OTPs, authenticator apps are not vulnerable to most threats found with SMS messaging, such as Signaling System 7 (SS7) attacks.
With two-factor authentication (2FA), users are required to use two types of authentication - such as a password and an SMS OTP. If more than two authentication factors are required, as often happens with high-value transactions or suspicious activity, the authentication practice is considered MFA.
SMS two-factor authentication is much safer than a sole reliance on usernames and passwords, However, other forms of authentication like FIDO2 and mobile authenticator apps are considered more secure than SMS messaging.
MFA is considered to be a very safe and secure identity verification practice. Microsoft reports that MFA can stop 99.9% of attacks on user accounts.
Start Today
See how Ping can help you deliver secure employee and customer experiences in a rapidly evolving digital world.